A Practical Guide to AI-Powered Predictive Maintenance Across Industries
Predictive maintenance (PdM) has shifted from a visionary concept to a board-level imperative. By combining industrial Internet-of-Things (IIoT) sensors, machine-learning models and real-time analytics, UK and EU organisations are cutting costs, slashing unplanned downtime and meeting tough sustainability goals. This guide explains the business value, key technologies, regulatory context and best-practice roadmap for successful PdM adoption—grounded in fresh 2025 data and framed for decision-makers.
Why Predictive Maintenance Now?
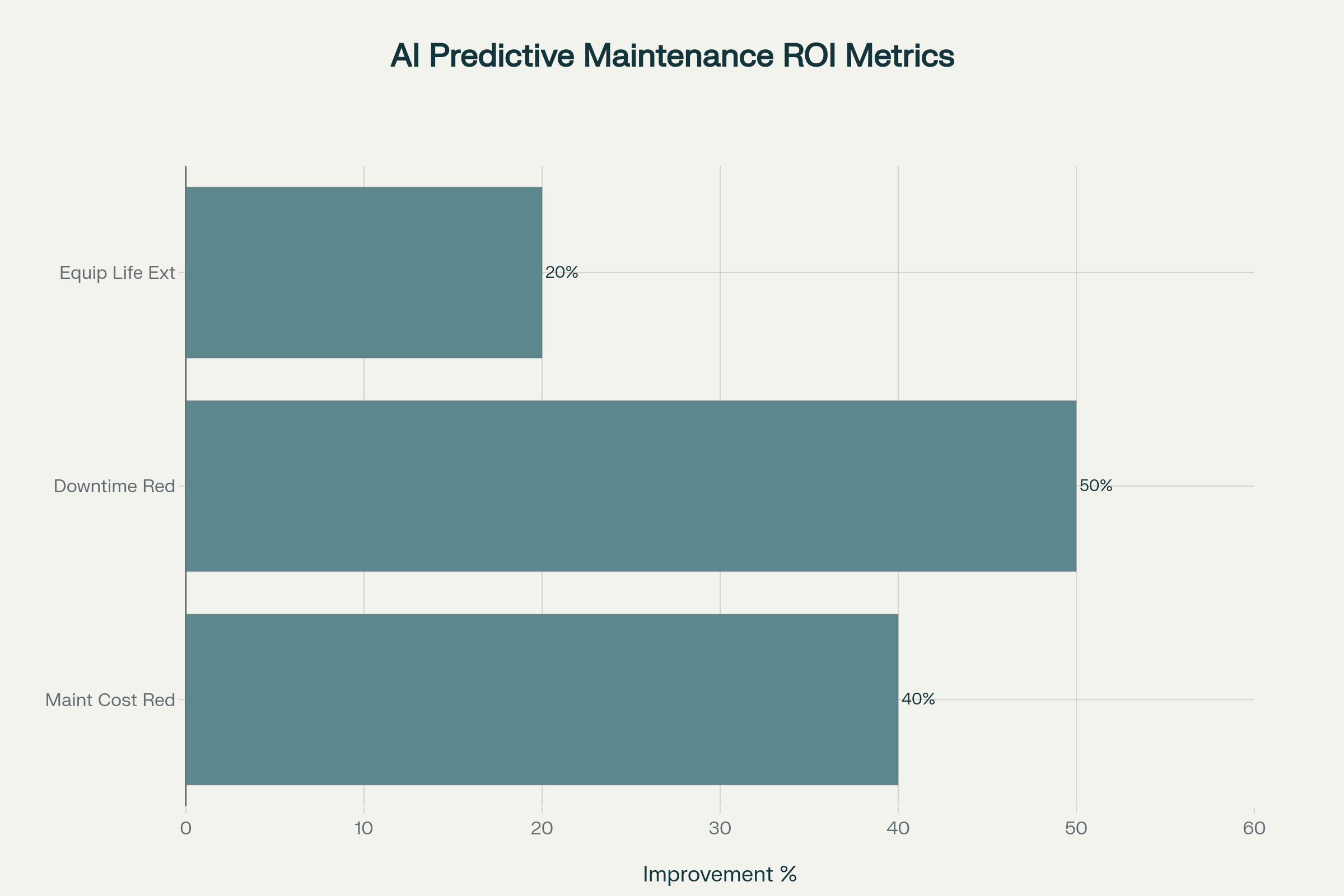
Unplanned outages will cost UK and EU manufacturers over £80 billion in 2025. Each lost production hour in automotive plants can exceed £1.6 million. In parallel, McKinsey’s global studies show that well-executed PdM programmes deliver 40% lower maintenance outlay, up to 50% less downtime and 20% longer asset life. For capital-intensive sectors—from energy to pharmaceuticals—these margins represent a decisive strategic edge.
The EU AI Act, effective from February 2025, classifies PdM as a “high-risk” industrial AI application requiring documented risk management, human oversight and cybersecurity assurance Article 5 guidance. Early movers therefore enjoy both operational resilience and future-proof compliance.
Typical ROI metrics based on industry studies (McKinsey)
How It Works: Technical Building Blocks
Data Acquisition and Edge Processing
IIoT sensors capture vibration, temperature, acoustic emissions and power draw at millisecond resolution.
Edge gateways compress and anonymise data to meet GDPR and reduce cloud latency.
Analytics and Machine Learning
Physics-informed neural networks and recurrent models learn failure signatures, enabling remaining-useful-life (RUL) predictions in hours or days rather than calendar-based cycles.
Graph databases contextualise assets, work orders and spare-parts inventory for rapid root-cause analysis.
Integration and Visualisation
Open APIs stream insights into enterprise asset-management (EAM) and ERP platforms, triggering automated work orders.
Operator dashboards prioritise alerts by financial risk, making AI outputs actionable for frontline engineers.
Market-Specific Use Cases
| Sector | High-Value Asset | Business Impact | Example Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy & Utilities | Gas turbines, wind turbines | Avoid black-start penalties and optimise fuel mix | £7.5m annual saving at one UK peaker plant |
| Automotive | Robotic weld cells, paint booths | Protect just-in-time schedules | 20–25 breakdowns/month cut by 45% |
| Pharmaceuticals | HVAC, clean-room compressors | Prevent batch loss and GMP non-compliance | £5–10m per major incident avoided |
| Rail & Transport | Rolling-stock doors, brakes | Reduce passenger delays and fines | 30% drop in service failures (Network Rail pilot) |
Regulatory and Governance Landscape
UK Health & Safety Executive (HSE) requires plant owners to implement “planned maintenance programmes and safe isolation procedures” HSE guidance. PdM directly addresses these duties by providing auditable inspection logs.
EU AI Act demands documented data lineage, bias testing, cybersecurity controls and human-in-the-loop overrides for all high-risk AI systems. Providers must perform conformity assessments and maintain technical files for at least ten years.
Net Zero Innovation Portfolio and AI for Decarbonisation Programme offer grant funding for PdM pilots that cut industrial emissions. Aligning projects with these schemes can unlock up to £150 k per proposal.
Risks and Mitigation Strategies
| Risk | Mitigation |
|---|---|
| Data Silos & Poor Quality | Conduct data readiness audits; deploy edge preprocessing to filter noise. |
| Cybersecurity Exposure | Adopt zero-trust OT networks; segment sensor traffic and apply IEC 62443 controls. |
| Model Drift | Schedule quarterly model-retraining using latest failure events; monitor drift dashboards. |
| Regulatory Non-Compliance | Embed AI governance frameworks aligned to EU AI Act; maintain model explainability documentation. |
| Change Management Resistance | Run cross-functional workshops; incentivise operators with uptime KPIs rather than reactive fixes. |
Best-Practice Roadmap for Deployment
Value Scoping – Prioritise assets with the highest downtime cost and carbon footprint.
Pilot & Benchmark – Deploy PdM on a small asset cohort; track KPIs such as mean-time-between-failures (MTBF).
Scale Securely – Extend to enterprise scale through central IoT platforms and cloud-edge hybrids; enforce role-based access.
Continuous Improvement – Integrate feedback loops between maintenance logs and model retraining for adaptive accuracy.
Regulatory Alignment – Document the AI life cycle, run bias tests and conduct annual compliance audits ahead of the EU AI Act 2026 milestones.
Data Nucleus Solutions Snapshot
Predictive Maintenance AI – Plug-and-play sensor ingestion, transfer-learning models and RNNs that have cut breakdowns by 70% for mid-sized manufacturers.
General Equipment Digital Twin – Cloud-native twins offering real-time 3-D visualisation, anomaly detection and useful-life prediction for SME industrial assets.
Energy & Asset Management Platform – Combines PdM with HVAC optimisation to curb emissions by 40% via reinforcement learning.
Solutions Deployment Framework – Rapid sprint-to-production methodology, embedding compliance and security by design across UK critical infrastructure sectors.
Actionable Insights
Start with a three-month pilot targeting one critical production line; success stories ease internal funding hurdles.
Quantify gains in cash terms—e.g., “£200 k spare-parts saving” resonates better than percentage metrics.
Align PdM with net-zero agendas to tap public grants and accelerate ESG reporting.
Treat models as living assets: allocate OPEX for monitoring, retraining and cybersecurity patching.
Conclusion
AI-driven predictive maintenance is no longer experimental. With £80 billion at stake across UK and EU manufacturing, and regulatory deadlines looming, organisations that act now will secure decisive ROI, resilience and sustainability advantages. By following a structured roadmap—grounded in robust data governance and change-management principles—business leaders can transform maintenance from cost centre to profit driver.
Disclaimer: This article is for information only and may change without notice. It is provided “as is,” without warranties (including merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose), and does not create any contractual obligations. Data Nucleus Ltd is not liable for any direct, indirect, incidental, special, consequential, or exemplary damages arising from use of or reliance on this document.
Data protection/UK GDPR: data-controller@datanucleus.co.uk